Join our translation project and help translate Zabbix documentation into your native language.
4 Secret user macros
Zabbix provides two options for protecting sensitive information in user macro values:
- Secret text
- Vault secret
Note that while the value of a secret macro is hidden, the value can be revealed through the use in items. For example, in an external script an 'echo' statement referencing a secret macro may be used to reveal the macro value to the frontend because Zabbix server has access to the real macro value. See also locations where secret macro values are unmasked.
Secret macros cannot be used in trigger expressions.
Secret text
Values of secret text macros are masked by the asterisks.
To make macro value 'secret', click on the button at the end of the value field and select the option Secret text.
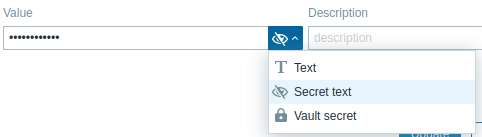
Once the configuration is saved, it will no longer be possible to view the value.
The macro value will be displayed as asterisks.
To enter a new value, hover over the value field and press Set new value button (appears on hover).

If you change macro value type or press Set new value, current value will be erased. To revert the original value, use the backwards arrow at the right end of the Value field  (only available before saving new configuration). Reverting the value will not expose it.
(only available before saving new configuration). Reverting the value will not expose it.
URLs that contain a secret macro will not work as the macro in them will be resolved as "******".
Vault secret
With Vault secret macros, the actual macro value is stored in an external secret management software (vault).
To configure a Vault secret macro, click on the button at the end of the Value field and select the option Vault secret.
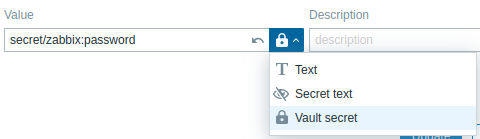
The macro value should point to a vault secret. The input format depends on the vault provider. For provider-specific configuration examples, see:
Vault secret values are retrieved by Zabbix server on every refresh of configuration data and then stored in the configuration cache.
To manually trigger refresh of secret values from a vault, use the 'secrets_reload' command-line option.
Zabbix proxy receives values of vault secret macros from Zabbix server on each configuration sync and stores them in its own configuration cache. The proxy never retrieves macro values from the vault directly. That means a Zabbix proxy cannot start data collection after a restart until it receives the configuration data update from Zabbix server for the first time.
Encryption must be enabled between Zabbix server and proxy; otherwise a server warning message is logged.
If a macro value cannot be retrieved successfully, the corresponding item using the value will turn unsupported.
Unmasked locations
This list provides locations of parameters where secret macro values are unmasked.
| Context | Parameter | |
|---|---|---|
| Items | ||
| Item | Item key parameters | |
| SNMP agent | SNMP community | |
| Context name (SNMPv3) | ||
| Security name (SNMPv3) | ||
| Authentication passphrase (SNMPv3) | ||
| Privacy passphrase (SNMPv3) | ||
| HTTP agent | URL | |
| Query fields | ||
| Post | ||
| Headers | ||
| Username | ||
| Password | ||
| SSL key password | ||
| Script | Parameters | |
| Script | ||
| Browser | Parameters | |
| Script | ||
| Database monitor | SQL query | |
| Telnet | Script | |
| Username, password | ||
| SSH | Script | |
| Username, password | ||
| Simple check | Username, password | |
| JMX | Username, password | |
| Item value preprocessing | ||
| JavaScript preprocessing step | Script | |
| Web scenarios | ||
| Web scenario | Variable value | |
| Header value | ||
| URL | ||
| Query field value | ||
| Post field value | ||
| Raw post | ||
| Web scenario authentication |
User | |
| Password | ||
| SSL key password | ||
| Connectors | ||
| Connector | URL | |
| Username | ||
| Password | ||
| Token | ||
| HTTP proxy | ||
| SSL certificate file | ||
| SSL key file | ||
| SSL key password | ||
| Network discovery | ||
| SNMP | ||
| SNMP community | ||
| Context name (SNMPv3) | ||
| Security name (SNMPv3) | ||
| Authentication passphrase (SNMPv3) | ||
| Privacy passphrase (SNMPv3) | ||
| Global scripts | ||
| Webhook | JavaScript script | |
| JavaScript script parameter value | ||
| Telnet | ||
| Username, password | ||
| SSH | ||
| Username, password | ||
| Script | Script | |
| Media types | ||
| Script | Script parameters | |
| Webhook | Parameters | |
| IPMI | ||
| Username | ||
| Password | ||
