16 Tworzenie niestandardowych nazw liczników wydajności dla VMware
Przegląd
Ścieżka licznika wydajności VMware ma format group/counter[rollup], gdzie:
group- grupa licznika wydajności, na przykład cpucounter- nazwa licznika wydajności, na przykład usagemhzrollup- typ metody agregacji (rollup) licznika wydajności, na przykład average
Tak więc powyższy przykład dałby następującą ścieżkę licznika: cpu/usagemhz[average]
Opisy grup liczników wydajności, nazwy liczników i typy agregacji można znaleźć w dokumentacji VMware.
Możliwe jest uzyskanie wewnętrznych nazw i tworzenie niestandardowych nazw liczników wydajności za pomocą pozycji typu skrypt w Zabbix.
Konfiguracja
- Utwórz wyłączony element skryptu na głównym hoście VMware (gdzie obecna jest pozycja eventlog[]) z następującymi parametrami:
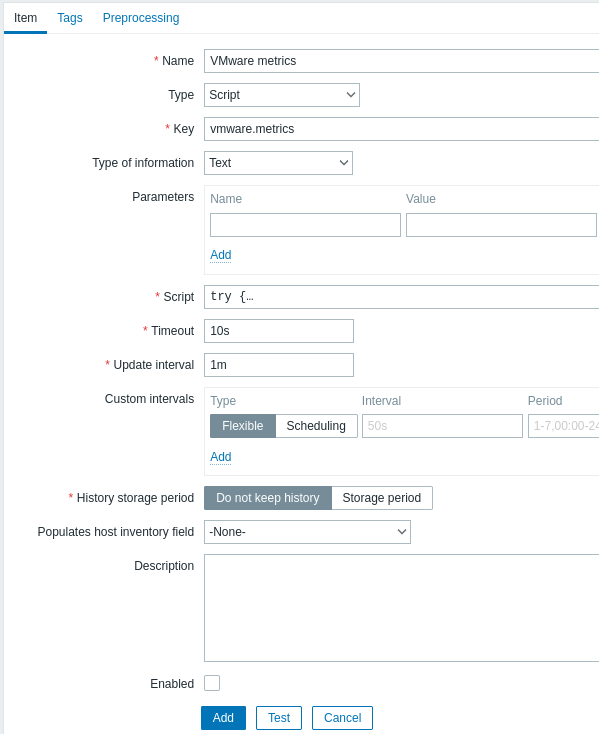
- Nazwa: VMware metrics
- Typ: Skrypt
- Klucz: vmware.metrics
- Typ informacji: Tekst
- Skrypt: skopiuj i wklej skrypt podany poniżej
- Przekroczenie czasu: 10
- Okres przechowywania historii: Nie przechowuj historii
- Włączone: niezaznaczone
Skrypt
try {
Zabbix.log(4, 'vmware metrics script');
var result, resp,
req = new HttpRequest();
req.addHeader('Content-Type: application/xml');
req.addHeader('SOAPAction: "urn:vim25/6.0"');
login = '<soapenv:Envelope xmlns:soapenv="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/" xmlns:urn="urn:vim25">\
<soapenv:Header/>\
<soapenv:Body>\
<urn:Login>\
<urn:_this type="SessionManager">SessionManager</urn:_this>\
<urn:userName>{$VMWARE.USERNAME}</urn:userName>\
<urn:password>{$VMWARE.PASSWORD}</urn:password>\
</urn:Login>\
</soapenv:Body>\
</soapenv:Envelope>'
resp = req.post("{$VMWARE.URL}", login);
if (req.getStatus() != 200) {
throw 'Response code: '+req.getStatus();
}
query = '<soapenv:Envelope xmlns:soapenv="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/" xmlns:urn="urn:vim25">\
<soapenv:Header/>\
<soapenv:Body>\
<urn:RetrieveProperties>\
<urn:_this type="PropertyCollector">propertyCollector</urn:_this>\
<urn:specSet>\
<urn:propSet>\
<urn:type>PerformanceManager</urn:type>\
<urn:pathSet>perfCounter</urn:pathSet>\
</urn:propSet>\
<urn:objectSet>\
<urn:obj type="PerformanceManager">PerfMgr</urn:obj>\
</urn:objectSet>\
</urn:specSet>\
</urn:RetrieveProperties>\
</soapenv:Body>\
</soapenv:Envelope>'
resp = req.post("{$VMWARE.URL}", query);
if (req.getStatus() != 200) {
throw 'Response code: '+req.getStatus();
}
Zabbix.log(4, 'vmware metrics=' + resp);
result = resp;
logout = '<soapenv:Envelope xmlns:soapenv="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/" xmlns:urn="urn:vim25">\
<soapenv:Header/>\
<soapenv:Body>\
<urn:Logout>\
<urn:_this type="SessionManager">SessionManager</urn:_this>\
</urn:Logout>\
</soapenv:Body>\
</soapenv:Envelope>'
resp = req.post("{$VMWARE.URL}",logout);
if (req.getStatus() != 200) {
throw 'Response code: '+req.getStatus();
}
} catch (error) {
Zabbix.log(4, 'vmware call failed : '+error);
result = {};
}
return result;Po skonfigurowaniu elementu, naciśnij przycisk Test, a następnie przycisk Pobierz wartość.

Skopiuj otrzymany XML do dowolnego formatera XML i znajdź pożądaną metrykę.
Przykład XML dla jednej metryki:
<PerfCounterInfo xsi:type="PerfCounterInfo">
<key>6</key>
<nameInfo>
<label>Usage in MHz</label>
<summary>CPU usage in megahertz during the interval</summary>
<key>usagemhz</key>
</nameInfo>
<groupInfo>
<label>CPU</label>
<summary>CPU</summary>
<key>cpu</key>
</groupInfo>
<unitInfo>
<label>MHz</label>
<summary>Megahertz</summary>
<key>megaHertz</key>
</unitInfo>
<rollupType>average</rollupType>
<statsType>rate</statsType>
<level>1</level>
<perDeviceLevel>3</perDeviceLevel>
</PerfCounterInfo>Użyj XPath, aby wydobyć ścieżkę licznika z otrzymanego XML. Dla powyższego przykładu, XPath będzie:
| Pole | XPath | Wartość |
|---|---|---|
| group | //groupInfo[../key=6]/key | cpu |
| counter | //nameInfo[../key=6]/key | usagemhz |
| rollup | //rollupType[../key=6] | average |
Wynikowa ścieżka licznika wydajności w tym przypadku to: cpu/usagemhz[average]

