Is this not what you were looking for? Switch to the current version or choose one from the drop-down menu.
8. Web monitoring
Overview
With Zabbix you can check several availability aspects of web sites.
To perform web monitoring Zabbix server must be initially configured with cURL (libcurl) support.
To activate web monitoring you need to define web scenarios. A web scenario consists of one or several HTTP requests or "steps". The steps are periodically executed by Zabbix server in a pre-defined order. If a host is monitored by proxy, the steps are executed by the proxy.
Since Zabbix 2.2 web scenarios are attached to hosts/templates in the same way as items, triggers, etc. That means that web scenarios can also be created on a template level and then applied to multiple hosts in one move.
The following information is collected in any web scenario:
- average download speed per second for all steps of whole scenario
- number of the step that failed
- last error message
The following information is collected in any web scenario step:
- download speed per second
- response time
- response code
For more details, see web monitoring items.
Data collected from executing web scenarios is kept in the database. The data is automatically used for graphs, triggers and notifications.
Zabbix can also check if a retrieved HTML page contains a pre-defined string. It can execute a simulated login and follow a path of simulated mouse clicks on the page.
Zabbix web monitoring supports both HTTP and HTTPS. When running a web scenario, Zabbix always follows redirects. All cookies are preserved during the execution of a single scenario.
Configuring a web scenario
To configure a web scenario:
- Go to: Configuration → Hosts (or Templates)
- Click on Web in the row of the host/template
- Click on Create scenario to the right (or on the scenario name to edit an existing scenario)
- Enter parameters of the scenario in the form
The Scenario tab allows you to configure the general parameters of a web scenario.
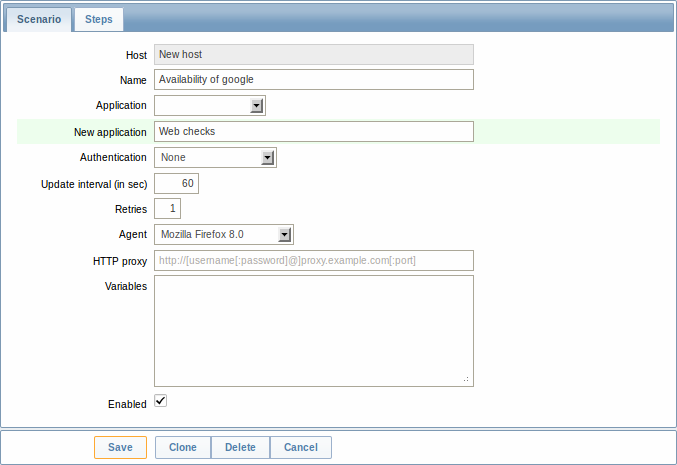
General parameters:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Host | Name of the host/template that the scenario belongs to. |
| Name | Unique scenario name. Starting with Zabbix 2.2, the name may contain supported macros. |
| Application | Select an application the scenario will belong to. Web scenario items will be grouped under the selected application in Monitoring → Latest data. |
| New application | Enter the name of a new application for the scenario. |
| Authentication | Authentication options. None - no authentication used. Basic authentication - basic authentication is used. NTLM authentication - NTLM (Windows NT LAN Manager) authentication is used. Selecting an authentication method will provide two additional fields for entering a user name and password. User macros can be used in user and password fields, starting with Zabbix 2.2. |
| Update interval (in sec) | How often the scenario will be executed, in seconds. |
| Retries | The number of attempts for executing web scenario steps. In case of network problems (timeout, no connectivity, etc) Zabbix can repeat executing a step several times. The figure set will equally affect each step of the scenario. Up to 10 retries can be specified, default value is 1. Note: Zabbix will not repeat a step because of a wrong response code or the mismatch of a required string. This parameter is supported starting with Zabbix 2.2. |
| Agent | Select a client agent. Zabbix will pretend to be the selected browser. This is useful when a website returns different content for different browsers. User macros can be used in this field, starting with Zabbix 2.2. |
| HTTP proxy | You can specify an HTTP proxy to use, using the format: http://[username[:password]@]proxy.mycompany.com[:port] By default, 1080 port will be used. If specified, the proxy will overwrite proxy related environment variables like http_proxy, HTTPS_PROXY. If not specified, the proxy will not overwrite proxy related environment variables. The entered value is passed on "as is", no sanity checking takes place. You may also enter a SOCKS proxy address. If you specify the wrong protocol, the connection will fail and the item will become unsupported. With no protocol specified, the proxy will be treated as an HTTP proxy. Note: Only simple authentication is supported with HTTP proxy. User macros can be used in this field. This parameter is supported starting with Zabbix 2.2. |
| Variables | List of scenario-level variables (macros) that may be used in scenario steps (URL, Post variables). They have the following format: {macro1}=value1 {macro2}=value2 {macro3}=regex:<regular expression> For example: {username}=Alexei {password}=kj3h5kJ34bd {hostid}=regex:hostid is ([0-9]+) If the value part starts with regex: then the part after it will be treated as a regular expression that will search the web page and, if found, store the match in the variable. Note that at least one subgroup must be present so that the matched value can be extracted. The macros can then be referenced in the steps as {username}, {password} and {hostid}. Zabbix will automatically replace them with actual values. Having variables that search a webpage for a regular expression match is supported starting with Zabbix 2.2. HOST.* macros and user macros can be used in this field, starting with Zabbix 2.2.Note: Variables are not URL-encoded. |
| Enabled | The scenario is active if this box is checked, otherwise - disabled. |
If HTTP proxy field is left empty, another way for using an HTTP proxy is to set proxy related environment variables.
For HTTP checks - set the http_proxy environment variable for the Zabbix server user. For example, //http_proxy=http:%%//%%proxy_ip:proxy_port//.
For HTTPS checks - set the HTTPS_PROXY environment variable. For example, //HTTPS_PROXY=http:%%//%%proxy_ip:proxy_port//. More details are available by running a shell command: # man curl.
The Steps tab allows you to configure the web scenario steps. To add a web scenario step, click on Add.
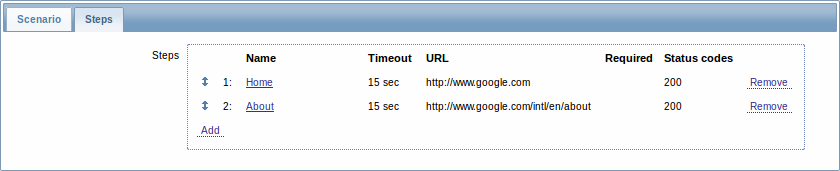
Configuring steps
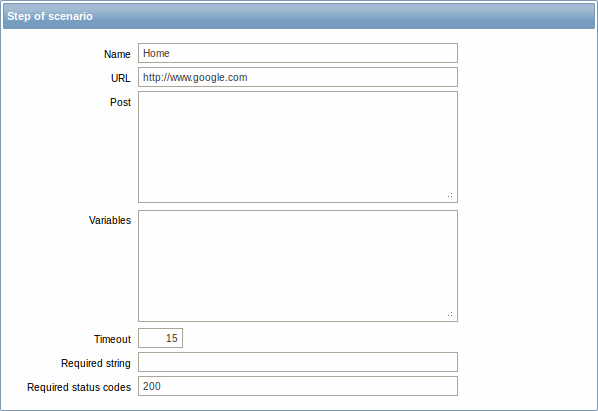
Step parameters:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Unique step name. Starting with Zabbix 2.2, the name may contain supported macros. |
| URL | URL to connect to and retrieve data. For example: http://www.zabbix.com https://www.google.com GET variables can be passed in the URL parameter. Starting with Zabbix 2.2, this field may contain supported macros. |
| Post | HTTP POST variables, if any. For example: id=2345&userid={user} If {user} is defined as a macro of the web scenario, it will be replaced by its value when the step is executed. The information will be sent as is, variables are not URL-encoded. Starting with Zabbix 2.2, this field may contain supported macros. |
| Variables | List of step-level variables (macros) that may be used for GET and POST functions. Step-level variables override scenario-level variables or variables from the previous step. However, the value of a step-level variable only affects the step after (and not the current step). They have the following format: {macro}=value {macro}=regex:<regular expression> For more information see variable description on the scenario level. Having step-level variables is supported starting with Zabbix 2.2. Note: Variables are not URL-encoded. |
| Timeout | Zabbix will not spend more than the set amount of seconds on processing the URL. Actually this parameter defines maximum time for making connection to the URL and maximum time for performing an HTTP request. Therefore, Zabbix will not spend more than 2 x Timeout seconds on the step. For example: 15 |
| Required string | Required regular expression pattern. Unless retrieved content (HTML) matches the required pattern the step will fail. If empty, no check on required string is performed. For example: Homepage of Zabbix Welcome.*admin Note: Referencing regular expressions created in the Zabbix frontend is not supported in this field. Starting with Zabbix 2.2, this field may contain supported macros. |
| Required status codes | List of expected HTTP status codes. If Zabbix gets a code which is not in the list, the step will fail. If empty, no check on required status codes is performed. For example: 200,201,210-299 Starting with Zabbix 2.2, user macros can be used in this field. |
Any changes in web scenario steps will only be saved when the whole scenario is saved.
See also a real-life example of how web monitoring steps can be configured.
Display
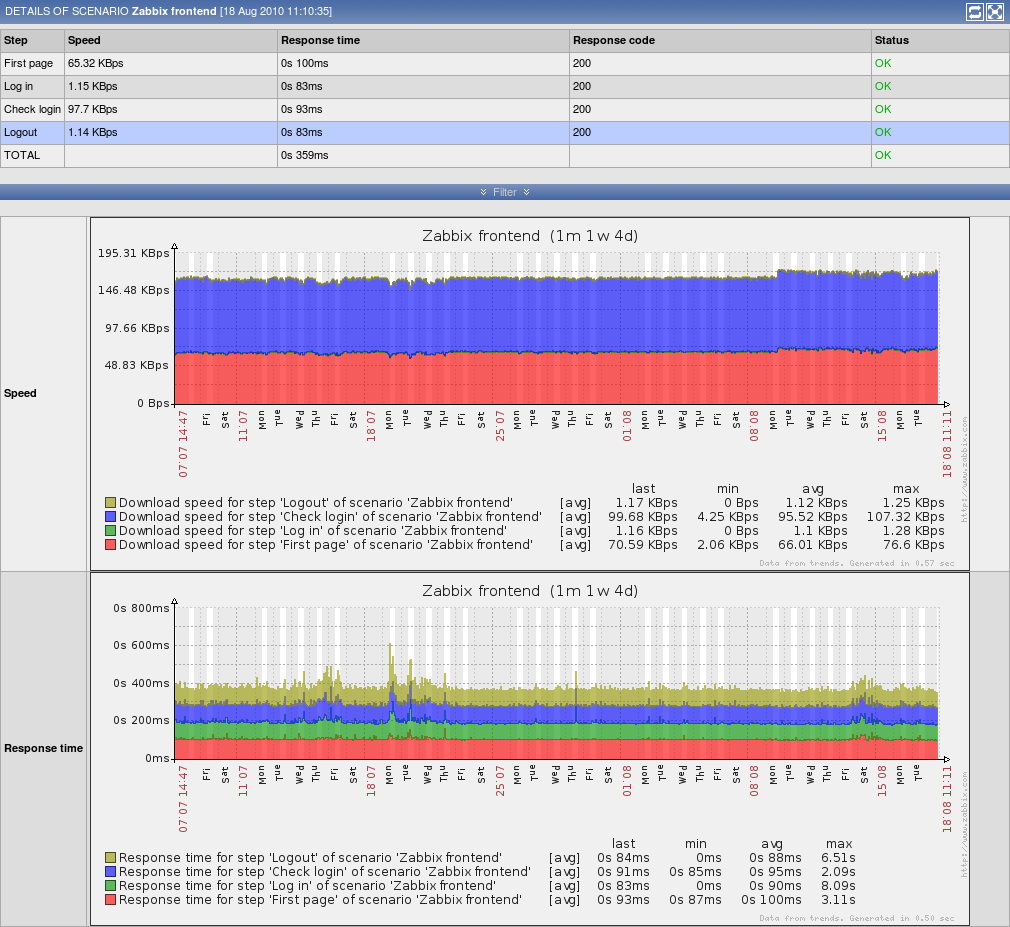
To view detailed data of defined web scenarios, go to Monitoring → Web or Latest data. Click on the scenario name to see more detailed statistics.
An overview of web monitoring scenarios can be viewed in Monitoring → Dashboard.

