Is this not what you were looking for? Switch to the current version or choose one from the drop-down menu.
3 User groups
Overview
User groups allow to group users both for organizational purposes and for assigning permissions to data. Permissions to monitoring data of host groups are assigned to user groups, not individual users.
It may often make sense to separate what information is available for one group of users and what - for another. This can be accomplished by grouping users and then assigning varied permissions to host groups.
A user can belong to any amount of groups.
Configuration
To configure a user group:
- Go to Administration → Users
- Select User groups from the dropdown to the right
- Click on Create group (or on the group name to edit an existing group)
- Edit group attributes in the form
The User group tab contains general group attributes:
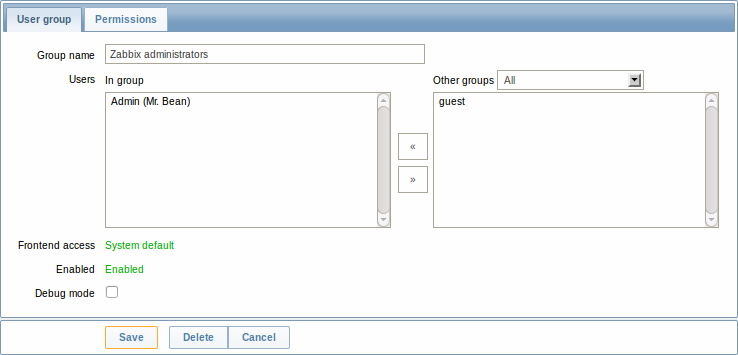
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Group name | Unique group name. |
| Users | The In group block contains a listing of the members of this group. To add users to the group select them in the Other groups block and click on <<. |
| Frontend access | How the users of the group are authenticated. System default - use default authentication Internal - use Zabbix authentication. Ignored if HTTP authentication is set Disabled - access to Zabbix GUI is forbidden |
| Users status | Status of group members: Enabled - users are active Disabled - users are disabled |
| Debug mode | Mark this checkbox to activate debug mode for the users. |
The Permissions tab allows you to specify user group access to host group (and thereby host) data:
| Composing permissions | Click on Add beneath the respective list to specify the host groups that the user group will have access to on the level of: Read-write - read-write access to a host group Read – read-only access to a host group Deny – access to a host group denied |
| Calculated permissions | Depending on the permissions set above, Calculated permissions will display all host groups and all hosts that the user group has access to on the level of: Read-write - host groups with read-write access Read - host groups with read-only access Deny - host groups with access denied |
Host access from several user groups
A user may belong to any number of user groups. These groups may have different access permissions to hosts.
Therefore, it is important to know what hosts an unprivileged user will be able to access as a result. For example, let us consider how access to host X (in Hostgroup 1) will be affected in various situations for a user who is in user groups A and B.
- If Group A has only Read access to Hostgroup 1, but Group B Read-write access to Hostgroup 1, the user will get Read-write access to 'X'.
“Read-write” permissions have precedence over “Read” permissions starting with Zabbix 2.2.
- In the same scenario as above, if 'X' is simultaneously also in Hostgroup 2 that is denied to Group A or B, access to 'X' will be unavailable, despite a Read-write access to Hostgroup 1.
- If Group A has no permissions defined and Group B has a Read-write access to Hostgroup 1, the user will get Read-write access to 'X'.
- If Group A has Deny access to Hostgroup 1 and Group B has a Read-write access to Hostgroup 1, the user will get access to 'X' denied.
Other details
- An Admin level user with Read-write access to a host will not be able to link/unlink templates, if he has no access to the Templates group. With Read access to Templates group he will be able to link/unlink templates to the host, however, will not see any templates in the template list and will not be able to operate with templates in other places.
- An Admin level user with Read access to a host will not see the host in the configuration section host list; however, the host triggers will be accessible in IT service configuration.
- Any non-Zabbix Super Admin user (including 'guest') can see network maps as long as the map is empty or has only images. When hosts, host groups or triggers are added to the map, permissions are respected. The same applies to screens and slideshows as well. The users, regardless of permissions, will see any objects that are not directly or indirectly linked to hosts.
- Zabbix server will not send notifications to users defined as action operation recipients if access to the concerned host is explicitly "denied" or if there are no rights defined to the host.

