2 Remote commands
Overview
With remote commands you can define that a certain pre-defined command is automatically executed on the monitored host upon some condition.
Thus remote commands are a powerful mechanism for smart pro-active monitoring.
In the most obvious uses of the feature you can try to:
- Automatically restart some application (web server, middleware, CRM) if it does not respond
- Use IPMI 'reboot' command to reboot some remote server if it does not answer requests
- Automatically free disk space (removing older files, cleaning /tmp) if running out of disk space
- Migrate a VM from one physical box to another depending on the CPU load
- Add new nodes to a cloud environment upon insufficient CPU (disk, memory, whatever) resources
Configuring an action for remote commands is similar to that for sending a message, the only difference being that Zabbix will execute a command instead of sending a message.
Remote commands can be executed by Zabbix server, proxy or agent. Remote commands on Zabbix agent can be executed directly by Zabbix server or through Zabbix proxy. Both on Zabbix agent and Zabbix proxy remote commands are disabled by default. They can be enabled by:
- adding an
AllowKey=system.run[*]parameter in agent configuration; - setting the EnableRemoteCommands parameter to '1' in proxy configuration.
Remote commands executed by Zabbix server are run as described in Command execution including exit code checking.
Remote commands are executed even if the target host is in maintenance.
Remote command limit
Remote command limit after resolving all macros depends on the type of database and character set (non-ASCII characters require more than one byte to be stored):
| Database | Limit in characters | Limit in bytes |
|---|---|---|
| MySQL | 65535 | 65535 |
| PostgreSQL | 65535 | not limited |
| SQLite (only Zabbix proxy) | 65535 | not limited |
Remote command execution output (return value) is limited to 16MB (including trailing whitespace that is truncated). IPMI remote command limit is based on the installed IPMI library. Note that database limits apply to all remote commands.
Configuration
Those remote commands that are executed on Zabbix agent (custom scripts) must be first enabled in the agent configuration.
Make sure that the AllowKey=system.run[<command>,*] parameter is added for each allowed command in agent configuration to allow specific command with nowait mode. Restart agent daemon if changing this parameter.
Then, when configuring a new action in Alerts → Actions → Trigger actions:
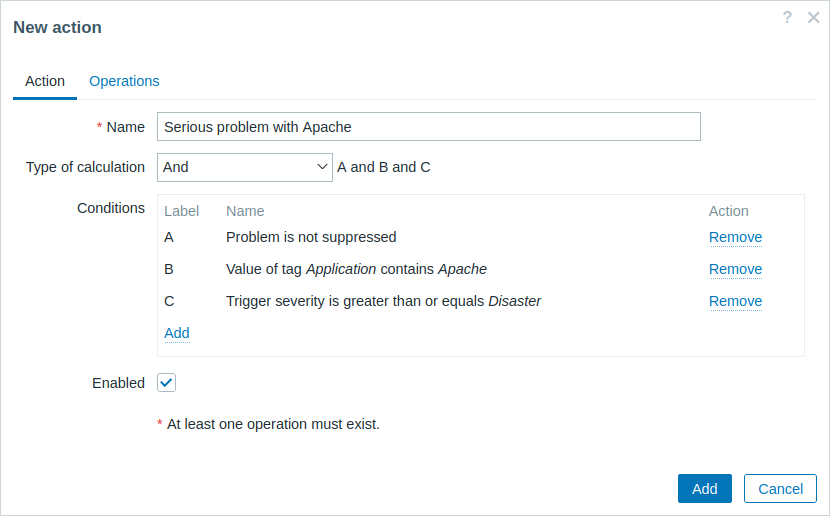
- Define the appropriate conditions, for example, set that the action is activated upon any disaster problems with one of Apache applications.
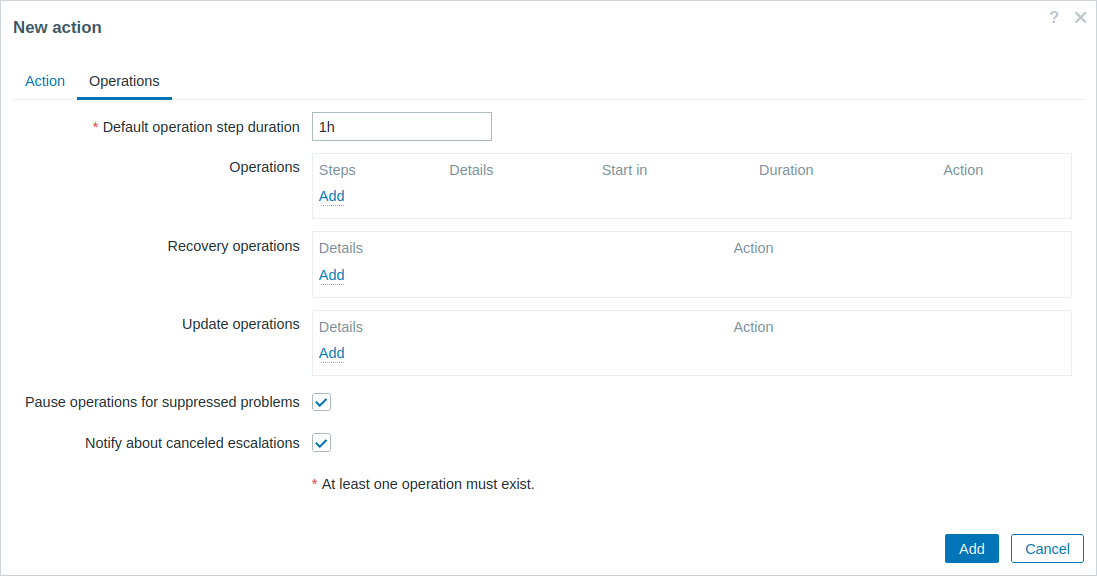
- In the Operations tab, click on Add in the Operations, Recovery operations, or Update operations block.
- Select one of the predefined scripts from the Operation dropdown list and set the Target list for the script.
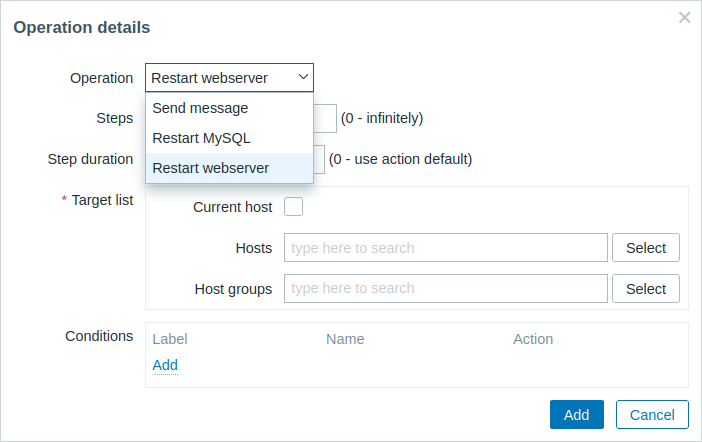
Predefined scripts
Scripts that are available for action operations (webhook, script, SSH, Telnet, IPMI) are defined in global scripts.
For example:
In this case, Zabbix will try to restart an Apache process. With this command, make sure that the command is executed on Zabbix agent (click the Zabbix agent button against Execute on).
Note the use of sudo - Zabbix user does not have permissions to restart system services by default. See below for hints on how to configure sudo.
Starting with Zabbix agent 7.0, remote commands can also be executed on an agent that is operating in active mode. Zabbix agent - whether active or passive - should run on the remote host, and executes the commands in background.
Remote commands on Zabbix agent are executed without timeout by the system.run[,nowait] key and are not checked for execution results. On Zabbix server and Zabbix proxy, remote commands are executed with timeout as set in the TrapperTimeout parameter of zabbix_server.conf or zabbix_proxy.conf file and are checked for execution results. For additional information, see Script timeout.
Access permissions
Make sure that the 'zabbix' user has execute permissions for configured commands. One may be interested in using sudo to give access to privileged commands. To configure access, execute as root:
Example lines that could be used in sudoers file:
# allows 'zabbix' user to run all commands without password.
zabbix ALL=NOPASSWD: ALL
# allows 'zabbix' user to restart apache without password.
zabbix ALL=NOPASSWD: /etc/init.d/apache restartOn some systems sudoers file will prevent non-local users from executing commands. To change this, comment out requiretty option in /etc/sudoers.
Remote commands with multiple interfaces
If the target system has multiple interfaces of the selected type (Zabbix agent or IPMI), remote commands will be executed on the default interface.
It is possible to execute remote commands via SSH and Telnet using another interface than the Zabbix agent one. The available interface to use is selected in the following order:
- Zabbix agent default interface
- SNMP default interface
- JMX default interface
- IPMI default interface
IPMI remote commands
For IPMI remote commands the following syntax should be used:
where
- <command> - one of IPMI commands without spaces
- <value> - 'on', 'off' or any unsigned integer. <value> is an optional parameter.
Examples
Examples of global scripts that may be used as remote commands in action operations.
Example 1
Restart of Windows on certain condition.
In order to automatically restart Windows upon a problem detected by Zabbix, define the following script:
| Script parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Scope | 'Action operation' |
| Type | 'Script' |
| Command | c:\windows\system32\shutdown.exe -r -f |
Example 2
Restart the host by using IPMI control.
| Script parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Scope | 'Action operation' |
| Type | 'IPMI' |
| Command | reset |
Example 3
Power off the host by using IPMI control.
| Script parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Scope | 'Action operation' |
| Type | 'IPMI' |
| Command | power off |
