Is this not what you were looking for? Switch to the current version or choose one from the drop-down menu.
Best practices for secure Zabbix setup
Overview
This section contains best practices that should be observed in order to set up Zabbix in a secure way.
The practices contained here are not required for the functioning of Zabbix. They are recommended for better security of the system.
Secure user for Zabbix agent
In the default configuration, Zabbix server and Zabbix agent processes share one 'zabbix' user. If you wish to make sure that the agent cannot access sensitive details in server configuration (e.g. database login information), the agent should be run as a different user:
- Create a secure user
- Specify this user in the agent configuration file ('User' parameter)
- Restart the agent with administrator privileges. Privileges will be dropped to the specified user.
UTF-8 encoding
UTF-8 is the only encoding supported by Zabbix. It is known to work without any security flaws. Users should be aware that there are known security issues if using some of the other encodings.
Setting up SSL for Zabbix frontend
On RHEL/Centos, install mod_ssl package:
Create directory for SSL keys:
Create SSL certificate:
openssl req -x509 -nodes -days 365 -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout /etc/httpd/ssl/private/apache-selfsigned.key -out /etc/httpd/ssl/apache-selfsigned.crtFill out the prompts appropriately. The most important line is the one that requests the Common Name. You need to enter the domain name that you want to be associated with your server. You can enter the public IP address instead if you do not have a domain name. We will use example.com in this article.
Country Name (2 letter code) [XX]:
State or Province Name (full name) []:
Locality Name (eg, city) [Default City]:
Organization Name (eg, company) [Default Company Ltd]:
Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []:
Common Name (eg, your name or your server's hostname) []:example.com
Email Address []:Edit Apache SSL configuration:
/etc/httpd/conf.d/ssl.conf
DocumentRoot "/usr/share/zabbix"
ServerName example.com:443
SSLCertificateFile /etc/httpd/ssl/apache-selfsigned.crt
SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/httpd/ssl/private/apache-selfsigned.keyRestart the Apache service to apply the changes:
Enabling Zabbix on root directory of URL
Add a virtual host to Apache configuration and set permanent redirect for document root to Zabbix SSL URL. Do not forget to replace example.com with the actual name of the server.
/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
#Add lines
<VirtualHost *:*>
ServerName example.com
Redirect permanent / http://example.com
</VirtualHost>Restart the Apache service to apply the changes:
Disabling web server information exposure
It is recommended to disable all web server signatures as part of the web server hardening process. The web server is exposing software signature by default:
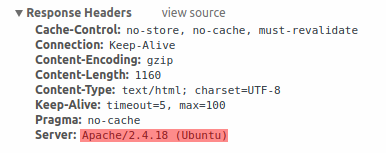
The signature can be disabled by adding two lines to the Apache (used as an example) configuration file:
PHP signature (X-Powered-By HTTP header) can be disabled by changing the php.ini configuration file (signature is disabled by default):
Web server restart is required for configuration file changes to be applied.
Additional security level can be achieved by using the mod_security (package libapache2-mod-security2) with Apache. mod_security allows to remove server signature instead of only removing version from server signature. Signature can be altered to any value by changing "SecServerSignature" to any desired value after installing mod_security.
Please refer to documentation of your web server to find help on how to remove/change software signatures.
Disabling default web server error pages
It is recommended to disable default error pages to avoid information exposure. Web server is using built-in error pages by default:
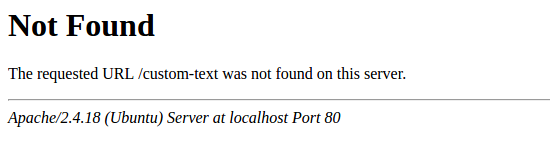
Default error pages should be replaced/removed as part of the web server hardening process. The "ErrorDocument" directive can be used to define a custom error page/text for Apache web server (used as an example).
Please refer to documentation of your web server to find help on how to replace/remove default error pages.
Removing web server test page
It is recommended to remove the web server test page to avoid information exposure. By default, web server webroot contains a test page called index.html (Apache2 on Ubuntu is used as an example):
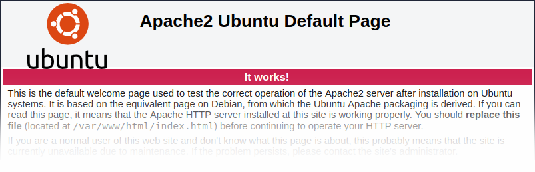
The test page should be removed or should be made unavailable as part of the web server hardening process.

